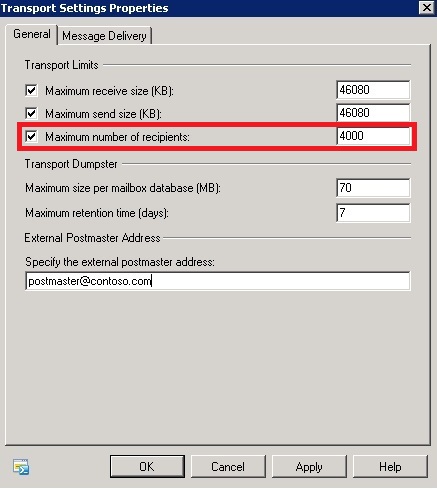
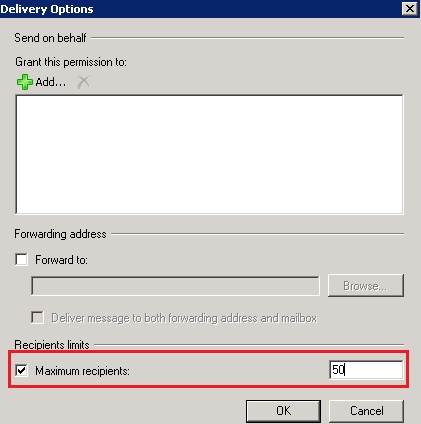
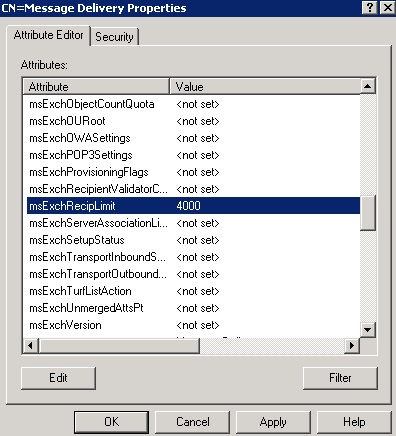
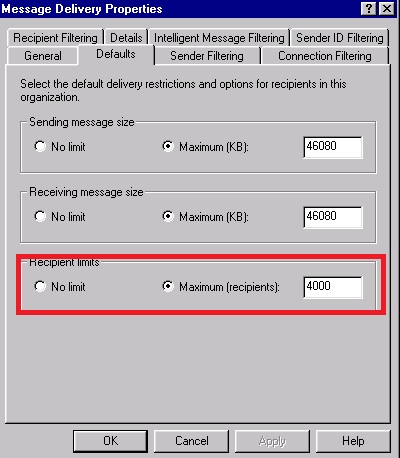
Jika pada edisi PC Plus sebelumnya
penulis membahas bagaimana mengurangi atau memperkecil hardisk pada
kesempatan kali ini penulis ingin membahas bagaimana menambah partisi
pada hyper-V. Seperti sering kita alami ketika menggunakan komputer
fisik kadangkala alokasi hardisk tidak sesuai dengan perkembangan waktu
yang mana data semakin bertambah besar, tentu hal ini juga mebutuhkan
ruang yang lebih besar pada hardisk. Jika pada komputer fisik kita tidak
bisa mengurangi atau menambah kapasitas hardisk secara langsung,
kecuali kita menambahkan hardisk baru maka pada lingkungan virtual semua
itu dapat di lakukan.
Ingat, yang penulis
bahas di sini bukan menambah atau merubah partisi hardisk misal Drive
C:, D: E: dan seterusnya, tetapi menambahkan kapasitas hardisk, jika
ingin menambah atau menguangi partisi pada partisi hardisk (drive) anda
bisa menggunakan Disk Management atau menggunakan program Partition
Manager lain seperti Partition Magic, EaseUS Partition manager, Paragon
Partition Manager dan lain lain.
Bagi yang
sudah biasa bekerja pada lingkungan virtualisasi pasti pernah mengalami,
dimana kapasitas hardisk pada salah satu atau beberapa virtual mesin
butuh kapasitas tambahan. Kebutuhan tambahan kapasitas hardisk
disebabkan oleh pengalokasian kapasitas hardisk yang terlalu kecil,
mungkin untuk beberapa waktu yang lalu kapasitas hardisk masih
mencukupi, tetapi seiring dengan berjalannya waktu file-file semakin
bertambah, database semakin membengkak dan update sistem operasi juga
membuat kapasitas hardisk menjadi penuh.
Pengalaman
penulis yang bekerja pada salah satu Cloud Computing service provider,
permintan penambahan kapasitas hardisk cukup sering, dari beberapa
pelaggan yang awalnya membeli paket VPS dengan spesifikasi yang kecil
atau sesuai kebutuhan waktu itu dengan seiring berjalannya waktu bisnis
mereka semakin berkembang dan beban VPS semakin bertambah, semua itu
tentu membutuhkan resource yang lebih seperti Memory, Core Processor dan
kapasitas Hardisk itu sendiri.
Pada tutorial
ini penulis ingin menambahkan kapasitas hardisk pada salah satu virtual
mesin dengan sistem operasi Windows 7, awalnya virtual mesin ini hanya
mempunyai kapasitas hardisk 127 GB kemudian panulis mengubah kapasitas
hardisk menjadi 150 GB.
1. Berikut tampilan hardisk pada virtual mesin Windows 7 dengan kapasitas awal 17 GB.
Gambar 1
2.
Untuk dapat menambahkan kapasitas hardisk, Shutdown Virtual mesin
terlebih dahulu. Proses shutdown bisa dalam virtual mesin atau dari
Hyper-V manager.
3. Kemudian pada Komputer Host buka Hyper-V manager, dari menu Start – Administrative Tools Plih Hyper-V Manager.
4. Pada Hyper-v Manager klik kanan pada virtual mesin yang di maksud kemudian pilih pilihan Settings….
Gambar 2
5. Pada halaman Settings, pilih menu IDE Controller kemudian pilih hardisk yang di maksud kemudian klik tombol Edit.
Kebetulan
pada gambar di bawah hanya terdapat satu hardisk jika terdapat beberapa
hardisk pada menu IDE Controller 0 atau IDE Controller 2 atau juga pada
SCSI Controller akan ada beberapa Hard drive, pastikan Hard Drive yang
akan di tambah kapsitasnya yang terpilih.
Gambar 3
6. Muncul halaman Edit Virtial Hard Disk Wizzard, pada Choose Action, karena kita ingin menambahkan kapasitas Hardisk maka pilih opsi Expand kemudian klik tombol Next.
Gambar 4
7. Pada halaman Configure Disk di sini anda dapat menentukan besaran kapasitas hardisk yang baru. Pada contoh di bawah penulish mengisikan New size: 150 GB dari kapasitas sebelumnya Current size is 127 GB kemudian klik tombol Next, berarti di sini penulis menambahkan kapasitas hardisk sebesar 23 GB.
Gambar 5
8. Kemudian pada halaan Summary, klik tombol Finish.
Gambar 6
9.
Sampai di sini proses penambahan Hardisk telah selesai, tetapi
kapastias yang kita tambahkan belum bisa di gunakan oleh pengguna, kita
perlu mengekspannya terlebih dahulu sebelum dapat di gunakan.
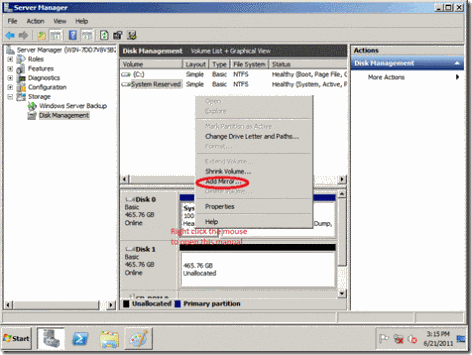
10. Buka Disk Management, dari menu Start klik kanan pada Computer kemudian pilih Manage.
Gambar 7
11. Pada halaman Disk management, perhatikan pada Disk 0, 23 GB kapasitas hardisk yang di tambahkan tadi masih dalam status Unallocated, langkah selanjutnya yaitu mengekspand drive C agar menjadi 150 GB.
Selain mengekspan Drive C anda juga dapat membuat partisi baru pada kapasitas hardisk yang kita tambhakan tadi.
Gambar 8
12. Untuk mengekspan Drive C, klik kanan pada Drive C kemudian pilih Extend Volume….
Gambar 9
13. Muncul halaman Welcome to the Extend Volume Wizzard kemudian klik tonbol Next.
14. Pada halaman Select Disks, secara default semua kapasitas hardisk yang kita tambahkan langsung di tambahkan semua, terlihat pada kolom Selected kemdudian klik tombol Next.
Jika
anda ingin hanya sebagian kapasitas hard disk di tambahkan pada Drive C
dan sisanya ingin di jadikan partisi baru, anda pat mengedit nilai paa
Select the amount of space in MB lebih kecil, kemudian sisanya anda
dapat jadikan partisi sendiri.
Gambar 10
15. Muncul halaman Completing the Extend Volume Wizzard klik Finish.
16.
Penambahan kapasitas hardisk telah selesai, klik kanan pada drive C
kapasitas hardisk telah menjadi 150 GB dan sudah tidak terdapat lagi
partisi unallocated. Selanjutnya pengguna dapat bekerja dengan kapasitas
hardisk yang baru
Gambar 11



![clip_image002[5] clip_image002[5]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEg0nPMWVzSEBBnF_U-mhLu4iCynns4wZRTjoA0GbFGhOLnF0SrVC9d3xL4fXO5PPaYH7uPbC2_kU367nmnSGPluyNdSQWF4UwYuQFz_B1P5JOcERMV2c-q0nQoqK9e4hMHykWg1yI5yB4fL/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[7] clip_image002[7]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiNSIC2XNYMfLi2Wqy7B2RIov1LM-wwDOnmbdKeja7DkTlVda0mfxT5mKfA5DuckwWtkSoDhm2OOzMSALwiFVq9yi_Dx65iax4NYHIiR5J_XSNGhfsV5f8btfyTtp19qZZzuZxPRuZASVUu/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[9] clip_image002[9]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjmgHJpFcjmH-0RGlgSc2dyKS85l4aJY6N5r_WBJxp3vxuBwOgOjbVqVLMU052NEf7jfBpCWufTqhcVBc-8rTJpXmP7BsmfyHsIVw7FDYfGBPGdWaHhXmkwOWQs4j9kjhKZi_OPzv0CUe9H/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[11] clip_image002[11]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEioyDNZF_YTGVVUZMiqKomLE4Xl1aQ1KVfGVO2i2au9juMpn1mgIjj57cNE3Ws-PMUJxBECfmugKBXFa-Lg7UIjbQDZQQcYMb80orqAWh3_iVai-Vqr_b8qfS6r9nHdWp-YaypWU1omYB7g/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[13] clip_image002[13]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiECIQetcHJvBOrdeD3zgnIEcP7dMOFXetsnYJVyfOf-vydFvYWp6OrBkdjbOHzs2Mn7B9DRZaje9uDm11O9CD9e7a1yW3WTd2xmL8QuM5_nc5Vg1UNPhNx0k9O-DmmjnO-XQsIBH3F5ty5/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[15] clip_image002[15]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjba-Qyk3D3mI58Vo2RP8JQzLNkx0eH6Z3LsZf9Wb9073RTPgwVsiqIsdl35pkLarsJscNy6_-gVUQSJS18XkygPgwrpkQw9BVWbCiZ_MyCYlE18gU32A7O-zXDmTlKlp5QCmtYAle0WhUh/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[17] clip_image002[17]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEinm1qm9_iNhxeAMTrfyFg61VhVoV7TU0wxnftraDA1X05m_NZHY-ayNkxMZB4tkpnR-hxJxPuBzYu4faNXWUPicXFRLVokvW3Vs0E6_4QrwSWYDRZ1xiBMBP78HeHh52n_1zEa91tj2g6Z/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[19] clip_image002[19]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEh8Hdzgmn7DPAdXta1-plvE4_ek-b8Y8E2RtvveiA5Nmfc005SUKwa5XRRyvZO2h7R-S_hH4TTU11HJO4xeaPym7pKRhqyO-zFMXCNJSx-xYwuZsDUap5SMqBWdkqErijCJ_cIFr8DNrAj2/?imgmax=800)